Neodymium magnets are renowned for their exceptional strength and versatile applications. This blog post will explore magnetizing neodymium, a crucial step in creating these powerful magnets. We’ll also provide frequently asked questions at the end of the article to address common concerns.

- Why Magnetize Neodymium Magnets?
- How to Magnetize Neodymium Magnets: The Magnetization Process
- Considerations for Neodymium Magnets Magnetization
- Do neodymium magnets have to be magnetized?
- How to remagnetize a magnet with electricity?
- How long does it take to remagnetize a magnet?
- How to remagnetize a magnet at home?
- In conclusion
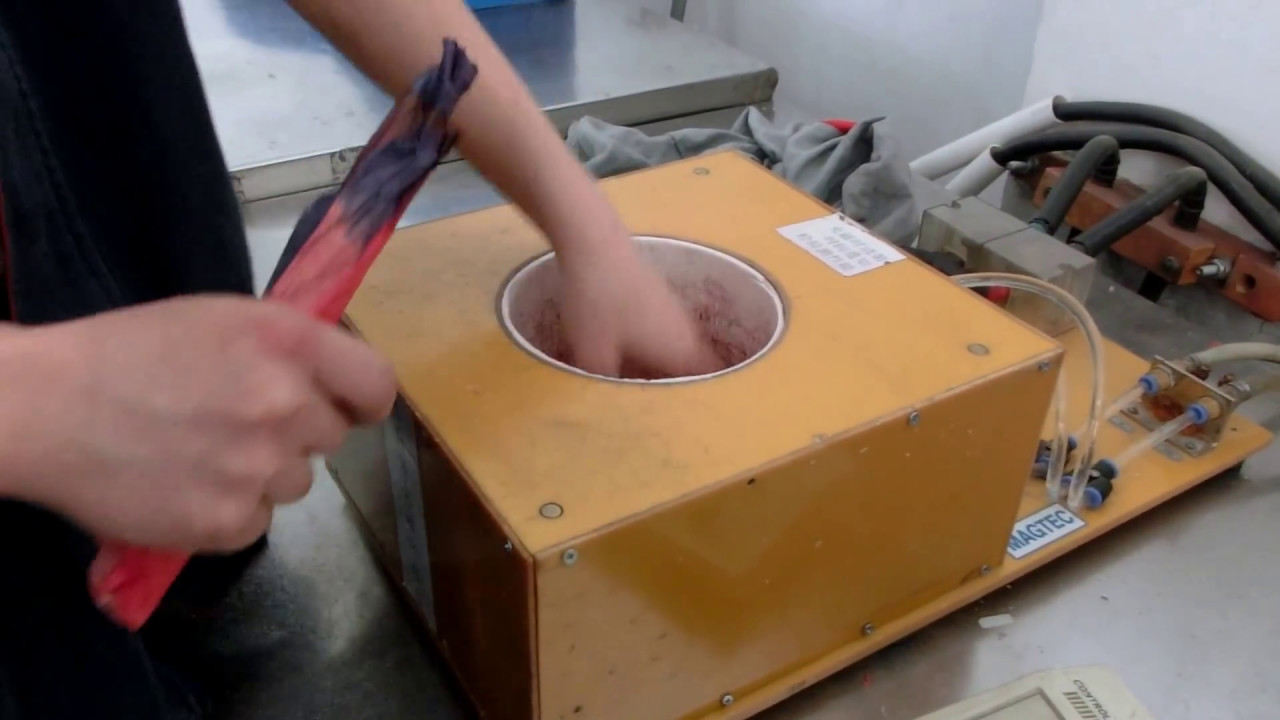
Why Magnetize Neodymium Magnets?
Magnetizing neodymium magnets allow them to exhibit their full magnetic potential, making them more efficient and effective in their applications. Additionally, it enables the magnet to maintain its magnetism over time.
How to Magnetize Neodymium Magnets: The Magnetization Process
Raw Materials and Production of the Neodymium Magnets
Neodymium magnets are constructed of a neodymium, iron, and boron alloy (NdFeB). The first stage in making a neodymium magnet is to melt the individual elements together to form the NdFeB alloy. After the alloy is created, it goes through many processes, including powder manufacturing, pressing, and sintering. The final product is a solid but unmagnetized NdFeB magnet.
Aligning the Magnetic Domains
To magnetize the magnet, align its magnetic domains first. To do this, subject the unmagnetized NdFeB magnet to a strong magnetic field known as “orientation.” During orientation, the magnetic field drives the magnetic domains inside the magnet to align in the same direction, resulting in a strong, homogeneous magnetic field.
Magnetizing the Neodymium Magnets
After aligning the magnetic domains, expose the magnet to an even stronger magnetic field called “magnetization.” A magnetizing coil or fixture typically generates this powerful magnetic field, permanently magnetizing the neodymium magnet. The magnetization process can be performed using either a pulse magnetizer or a continuous magnetizer, depending on factors such as the desired magnetization level and the size of the magnet.
Considerations for Neodymium Magnets Magnetization
Magnetization Direction
Neodymium magnets can be magnetized in various directions, including axially, diametrically, or radially. The desired magnetization direction must be determined before the magnetization process, as it will impact the final application and performance of the magnet.
Demagnetization and Re-magnetization
Remember that exposing neodymium magnets to high temperatures, strong opposing magnetic fields, or mechanical stress can partially or fully demagnetize them. If a neodymium magnet becomes demagnetized, you can often re-magnetize it using the same magnetization process described earlier.
Do neodymium magnets have to be magnetized?
Yes, you must magnetize it first to use neodymium as a permanent magnet. Neodymium, a type of rare-earth metal, possesses very strong magnetic properties. When you expose it to a magnetic field, the electrons within the neodymium align, creating a powerful magnetic force. This force is useful for various applications, such as motors, generators, and speakers.
Magnetizing neodymium is relatively simple, and you can do it with either an electromagnet or a permanent magnet. With an electromagnet, pass an electric current through the neodymium to align the electrons and create a strong magnetic field. Place the neodymium next to a permanent magnet and wait for it to react magnetically.
How to remagnetize a magnet with electricity?
Understand the Basics of Electromagnetism
Before attempting to remagnetize a magnet, it’s essential to understand the concept of electromagnetism. When an electric current flows through a wire, it creates a magnetic field around it. You can create an electromagnet with amplified magnetic strength by coiling the wire around a magnetic core, such as an iron nail. This electromagnet can be used to remagnetize your weakened magnet.
Gather the Necessary Materials
To remagnetize your magnet using electricity, you’ll need the following items:
a. A 12-volt DC power supply or a battery;
b. Insulated copper wire (20-22 gauge);
c. A nail or a piece of soft iron (to act as a magnetic core);
d. Electrical tape or alligator clips;
e. The weakened magnet you wish to remagnetize
Create an Electromagnet
Start by winding the insulated copper wire around the nail or iron core. Ensure the coils are tight and close together, with at least 50 turns. Leave enough wire at both ends to connect to the power supply. Attach one end of the wire to the positive terminal of the power supply and the other to the negative terminal using electrical tape or alligator clips.
Remagnetize Your Weakened Magnet
Place the electromagnet near the weakened magnet, making sure the north pole of the electromagnet is facing the north pole of the magnet you wish to remagnetize. Switch on the power supply to energize the electromagnet. Slowly move the electromagnet along the length of the weakened magnet several times, maintaining the same polarity orientation. This will help realign the magnetic domains within the weakened magnet.
Test Your Restored Magnet
After remagnetizing your magnet, switch off the power supply and disconnect the electromagnet. Test the magnet’s strength by trying to pick up small metal objects or by observing its attraction to another magnet. If the magnet still appears weak, repeat the process.
How long does it take to remagnetize a magnet?
While providing an exact timeframe for remagnetizing a magnet is difficult, the process typically takes a few seconds to several minutes. Smaller magnets, such as those used in household items, can usually be remagnetized in under a minute. Larger, industrial-strength magnets may require a longer time, ranging from a few minutes to several hours, depending on the method used and the magnet’s initial condition.
How to remagnetize a magnet at home?
Determine the Type of Magnet: Before you begin the remagnetization process, it’s essential to identify the type of magnet you have. Common household magnets are typically made of neodymium, ferrite, or alnico. Knowing the magnet’s material will help you choose the most effective remagnetization technique.
Choose the Right Method: There are two primary methods for remagnetizing a magnet at home:
a. Using a strong permanent magnet: This method suits small to medium-sized magnets of neodymium, ferrite, or alnico.
b. Using an electromagnet: This method works well for larger magnets or those that have lost a significant amount of their magnetism.

Remagnetize with a Strong Permanent Magnet: Follow these steps to remagnetize your magnet using a strong permanent magnet:
a. Identify the poles: Determine the weakened and strong permanent magnet’s north and south poles.
b. Align the magnets: Place the strong magnet’s north pole against the weakened magnet’s north pole.
c. Stroke the weakened magnet: Slowly and repeatedly stroke the weakened magnet with the strong magnet, moving in one direction only. This process helps realign the magnetic domains within the weakened magnet.
d. Test the magnet: Check the strength of the remagnetized magnet by trying to pick up small metal objects or observing its attraction to another magnet.
Remagnetize with an Electromagnet: If you choose to use an electromagnet, follow these steps:
a. Gather materials: You’ll need a 12-volt DC power supply or battery, insulated copper wire (20-22 gauge), a nail or a piece of soft iron, and electrical tape or alligator clips.
b. Create an electromagnet: Wind the copper wire around the nail or iron core, making at least 50 tight, close-together turns. Leave enough wire at both ends to connect to the power supply.
c. Connect the electromagnet: Attach one end of the wire to the positive terminal of the power supply and the other end to the negative terminal using electrical tape or alligator clips.
d. Remagnetize the weakened magnet: Place the electromagnet near the weakened magnet, with the electromagnet’s north pole facing the weakened magnet’s north pole. Turn on the power supply and move the electromagnet along the weakened magnet several times to realign the magnetic domains.
e. Test the magnet: Switch off the power supply, disconnect the electromagnet, and test the strength of the remagnetized magnet.
In conclusion
Magnetizing neodymium magnets involve creating the NdFeB alloy, aligning the magnetic domains through orientation, and then magnetizing the magnet using a powerful magnetic field. This intricate process requires specialized equipment and expertise to achieve the desired magnetization direction and strength. Understanding the magnetization process can help users make informed decisions about their neodymium magnets needs, whether for industrial, commercial, or personal applications.
FAQs
Can I magnetize a neodymium magnet at home?
Magnetizing a neodymium magnet demands specialized equipment and expertise, so attempting this at home is not recommended. Buy neodymium magnets that have already been magnetized instead, or speak with a reputable magnet manufacturer if you want bespoke magnetization.
How strong is the magnetic field required to magnetize a neodymium magnet?
The neodymium magnet’s size and quality determine the magnetic field’s strength required for magnetization. Typically, a magnetic field 2 to 5 times as strong as the magnet’s maximum energy product (BHmax) is needed.



